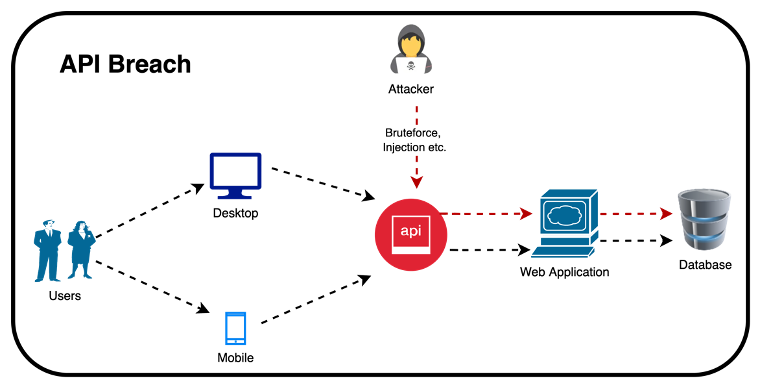
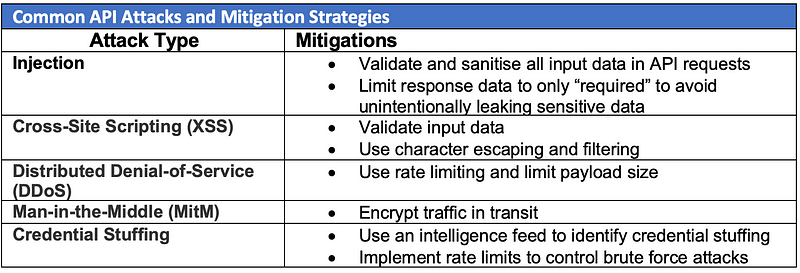
Your Weekly Cybersecurity Update (23 August 2024)
- OpenAI Blocks Iranian Influence Operation Using ChatGPT for U.S. Election Propaganda
- National Public Data Published Its Own Passwords
- Toyota confirms third-party data breach impacting customers
- Iranian Cyber Group TA453 Targets Jewish Leader with New AnvilEcho Malware
- Thousands of Websites Exposed AWS Credentials, Leading to Large-Scale Extortion Campaign
- GitHub Actions Exposing Authentication Tokens in Popular Open-Source Projects
OpenAI Blocks Iranian Influence Operation Using ChatGPT for U.S. Election Propaganda
OpenAI said its ChatGPT tool was used to create comments in English and Spanish, which were then posted on a dozen accounts on X and one on Instagram. Some of these comments were generated by asking its AI models to rewrite comments posted by other social media users.OpenAI Takes Action Against Iranian Influence Operation Using ChatGPT for U.S. Election PropagandaOpenAI made a significant move on Friday by shutting down a network of accounts tied to an alleged Iranian covert influence operation.
This operation reportedly utilised ChatGPT to generate content for the upcoming U.S. presidential election.”Using ChatGPT, the operation created content that focused on various topics, including commentary on candidates from both political parties in the U.S. presidential election. The content was then disseminated through social media accounts and websites,” OpenAI disclosed.
OpenAI noted that the generated content failed to garner substantial engagement, with most social media posts receiving minimal likes, shares, and comments. Additionally, little evidence supported the claim that the long-form articles created using ChatGPT were shared on social media platforms.
The articles, encompassing U.S. politics and global events, were published on five websites masquerading as progressive and conservative news outlets, indicating an attempt to target individuals from diverse political perspectives.
According to OpenAI, its ChatGPT tool was instrumental in producing comments in both English and Spanish, which were subsequently posted on a dozen X accounts and one Instagram account. Moreover, some of these comments were generated by instructing AI models to rewrite comments originally posted by other social media users.
National Public Data Published Its Own Passwords
Stunning new revelations have emerged about a shocking breach at National Public Data (NPD), a consumer data broker, exposing the sensitive information of hundreds of millions of Americans, including their Social Security Numbers, addresses, and phone numbers. It has come to light that another NPD data broker, with access to the same consumer records, mistakenly divulged the passwords to its back-end database in a file that was openly available from its website until today. This is becoming so common in all parts of the world, and this alarming development underscores the urgent need for enhanced security measures to protect consumers’ data.
Toyota confirms third-party data breach impacting customers
In a recent cyber incident, Toyota disclosed that a malicious actor unlawfully accessed and leaked 240 GB of data. This data breach included sensitive information belonging to both customers and employees. Notably, the breach did not stem from Toyota Motor North America’s own systems but rather from a misrepresented third-party entity. The threat actor claimed to have utilized the ADRecon tool to gain access to confidential data.
Toyota actively assists those impacted by the breach; however, additional specifics have not been divulged.
Iranian Cyber Group TA453 Targets Jewish Leader with New AnvilEcho Malware
Since late July 2024, threat actors sponsored by the Iranian state have been actively engaged in spear-phishing campaigns. Their primary target is a prominent Jewish figure, and their main objective is to distribute a sophisticated intelligence-gathering tool called AnvilEcho. This coordinated effort has garnered attention from multiple cybersecurity firms, each tracking the campaign under different aliases. These actions have been attributed to the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) of Iran and are believed to be aligned with the country’s political and military objectives.
are
Researchers at Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 discovered a large-scale extortion campaign targeting AWS environments. Attackers exploited insecurely stored environment variables on web servers to steal AWS access keys and credentials for various cloud services. They scanned over 110,000 domains, exposing over 90,000 unique environment variables, including sensitive credentials. The attackers used stolen credentials to move laterally within compromised environments, escalating privileges and deploying malicious scripts to exfiltrate data from S3 buckets.
The researchers emphasised the importance of secure configuration practices and recommended implementing logging, monitoring solutions, and temporary IAM roles to minimise the damage caused by compromised credentials. Businesses are urged to review and enhance their cloud security practices to prevent similar attacks.
GitHub Actions Exposing Authentication Tokens in Popular Open-Source Projects
A security vulnerability in GitHub Actions has exposed authentication tokens for high-profile open-source projects. It allows unauthorised access to private repositories, source code theft, and malicious code injection. Researchers discovered the vulnerability, named “ArtiPACKED,” and identified three contributing factors: default settings, misconfiguration, and lack of security checks. GitHub has not addressed the vulnerability, and developers are urged to secure their workflows. 14 large open-source projects are affected, and attackers could exploit the leaks to gain unauthorised access. Developers should avoid uploading sensitive directories, sanitize logs, review CI/CD workflows, and use the least privilege for access tokens. This incident emphasizes the importance of security best practices within CI/CD pipelines.